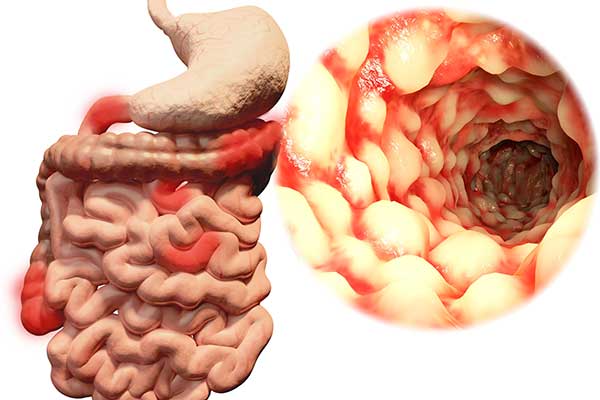
Crohn’s disease is most often diagnosed in adolescents and adults between the ages of 20-30. It affects both men and women equally, and there is some kind of genetic component to who develops Crohn’s disease and who doesn’t. In general, the small intestine is most commonly affected by the disease. Symptoms of Crohn’s disease are diarrhea, fever, fatigue, abdominal pain, blood in your stool, and unintended weight loss. There are many complications that can develop from Crohn’s disease if left untreated. Bowel obstructions, anal fissures, and malnutrition are just a few of the possible complications to be aware of.
Diagnosis of Crohn’s disease can be tricky; your medical doctor will likely diagnose you with the disease once other possible diagnoses have been ruled out through blood tests and stool tests, as well as through a procedure like a colonoscopy. Anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, immune system suppressants, and biologics are all commonly utilized treatments for Crohn’s disease symptom management. However, if symptoms are continuing to cause suffering on a daily basis, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the damaged sections of the bowel. At home, a healthy diet and effective stress management can help ease some of the symptoms without causing a disruption to daily life.